American muscle cars
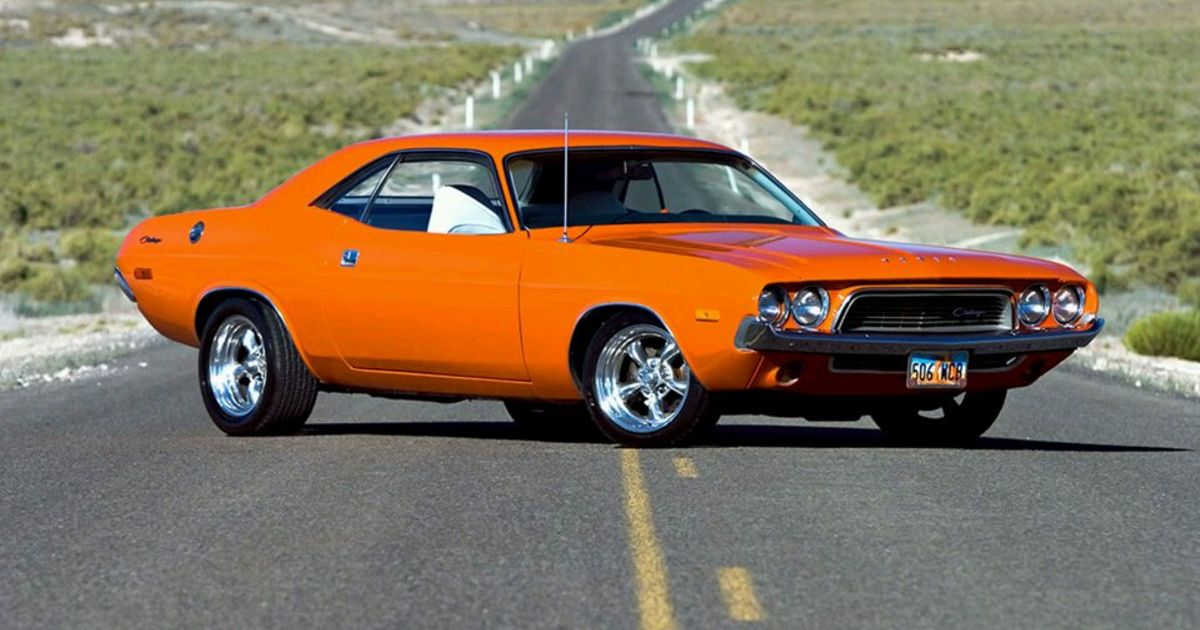

Car history of the United States could hardly be imagined without the era of the oil muscle cars, which lasted from the mid-60's to the early 70's of the last century. All the American manufacturers without exception produced muscle cars, and it was not only the representatives of the so-called "Big Three" (General Motors, Ford and Chrysler), but also the present known company AMC.
The term Muscle car (or muscular car) appeared in widespread use much later, in the late 1970s. Under this definition low-cost, medium-sized cars with the most powerful, exclusively 8-cylinder motors are understood. As a rule, manufacturers installed the most powerful engine from a larger car in a standard family sedan or an inexpensive coupe. The main criterion was a specific weight per a unit of power - no more than 6 kilograms per hp. In this case only the most powerful car model was considered a muscle car, in spite of engine volumes and dimensions.
Sometimes the powerful models of full-size sedans, as well as some compact cars, were referred to the muscle cars. The latter were named specifically - pony-cars. Among the most famous pony-cars FordMustang, DodgeChallenger, ChevroletCamaro, PlymouthBarracuda and others are distinguished. In addition to the above, the most powerful versions of these cars were still referred to the category of muscle cars (Plymouth `Cuda, Mustang GT, DodgeChallenger R/T).
Prehistory of muscle cars

Craving of young Americans to powerful and high-speed cars manifested itself before. In the 1950s, handicrafts produced hot-roads - charged versions of old cars. This required great financial costs and skills of the masters. At the same time, it was idle to expect serious high-speed indices from hot-roads.
By the early 1960s, young post-war generation had grown up in the United States, which was dissatisfied by slow-moving quiet family cars. European manufacturers produced expensive exclusive models for speed maniacs which were too expensive for pocketbook of simple people. American companies took a different road - they began to install motors of top versions in inexpensive cars.
At that time, gasoline in America was worth a penny, and huge fuel consumption did not bother anyone, nor harmful emissions that "gasoline eaters" with a 5- or even 7-liter engine polluted the atmosphere. At the state level, no one was particularly concerned about traffic safety. As a result, there appeared the cars with engine power of 300, 350 and even 450 horsepower. It was very much for a car that was not originally intended for such a monster. Therefore, accidents and fatalities involving muscle cars increased tens of times. By the way, accident statistics accumulated by insurance companies for ten years, forced them to increase rates for insurance of heavy-duty cars, which became one of the reasons for a decline era of muscle cars.
First muscle cars
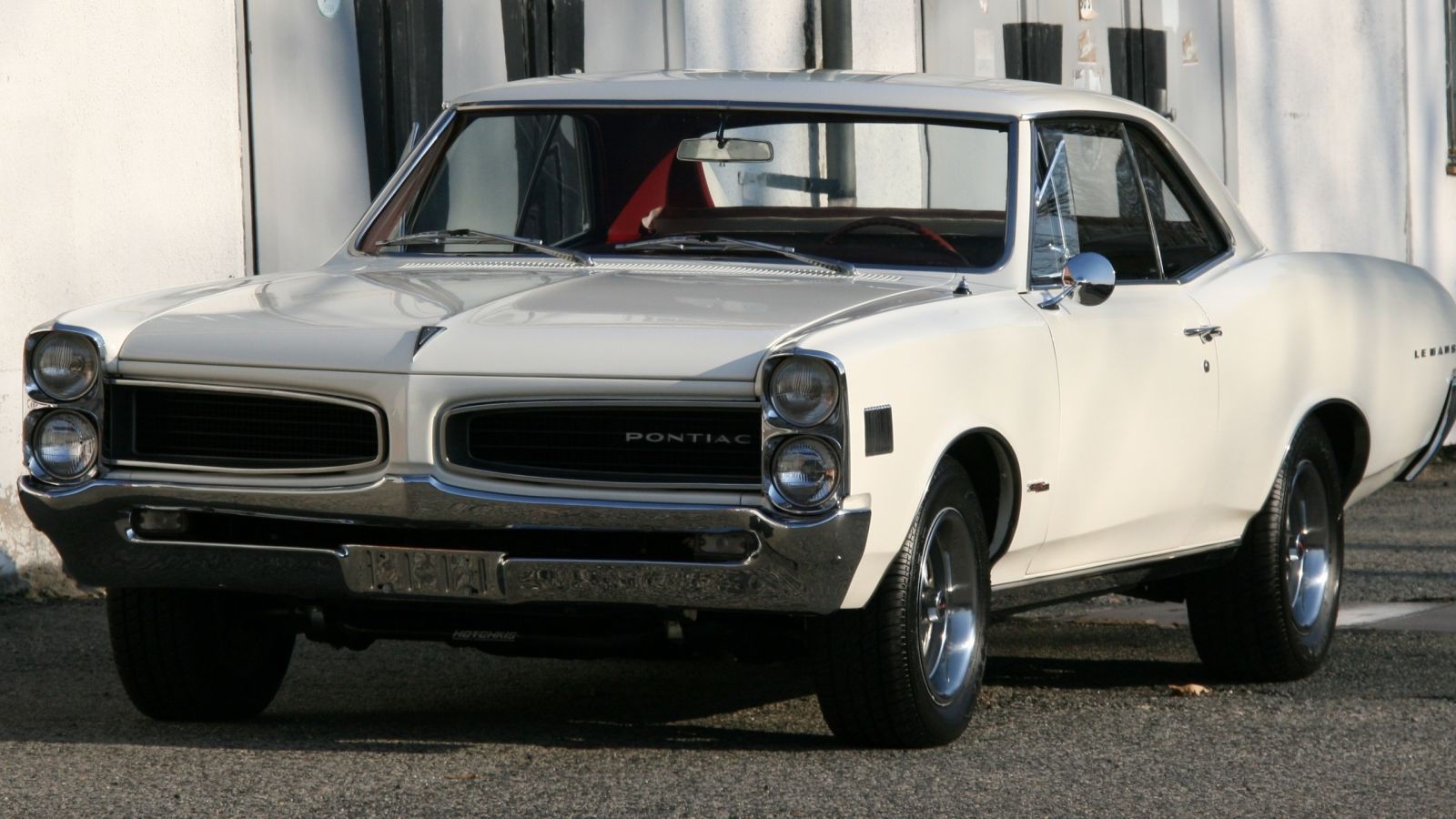

In the 1950s, power of serial motors on family sedans did not exceed 300 hp, but in the next decades there appeared Big-blocks with the volume of 5.7 liters, which showed at the stand 400 or more horsepower. Each manufacturer had such motors, but the first it was Pontiac where a powerful engine was installed on a standard coupe (sports division of General Motors). This happened in 1964 with Pontiac Tempest model, a powerful version of which had a 6-liter engine, 325 horsepower and a new name - GTO. In addition, a suspender was reinforced, appearance was changed, separate front seats were installed instead of sofas.
A year later Pontiac GTO became an independent model, and competitors rushed to catch it up. So, muscle cars appeared in all American companies - Ford Fairlane GT, Dodge Coronet R/T, Oldsmobile 442, Chevrolet Chevelle SS and others. Even Buick and Mercury started to produce muscle cars, which specialized in luxury cars, as well as, AMC (Rebel model).
The Golden Age
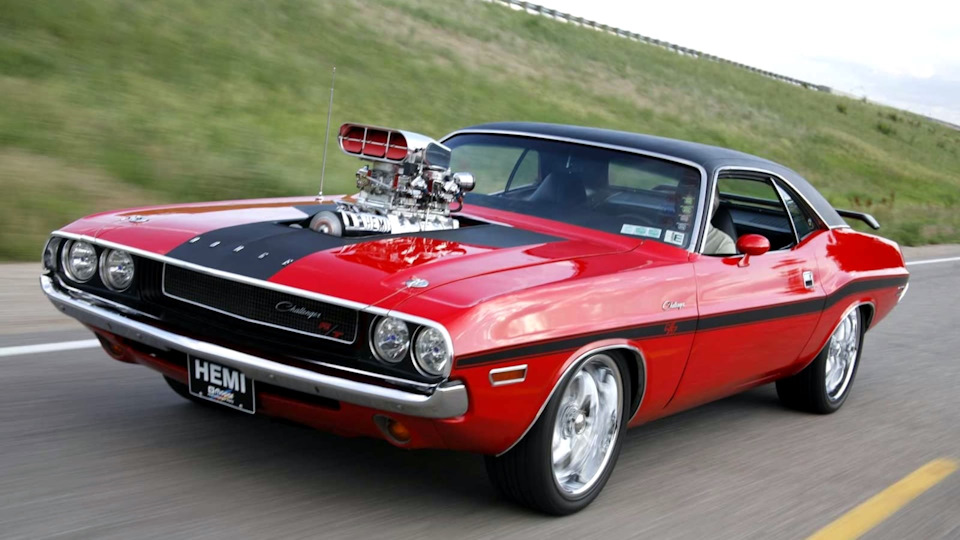

The end of the 1960s is considered a golden era in development of muscle cars. The cars of this type acquired a characteristic shape in the form of a bottle of Coca-Cola, so-called, Coca-Bottle style, a body type of fastback or fast-stop. In the first case, this is a two-door sedan with a smooth transition to the trunk or without a transition, in the second case it is a sedan or a coupe with a roof extended to the trunk. In addition, muscle cars were distinguished by an aggressive radiator enclosure, sometimes deeply recessed into a forecarriage line; they had built-in bumpers, lack of chrome in the lining, large air intakes and a number of other features.
During this period powerful versions of serial cars began to be produced not only on the basis of medium-sized cars. The cars of a compact class were used, as well as full-size sedans, vans and pickups. Among full-size muscle cars Chevrolet Impala SS, Ford Galaxie, Dodge Coronet R/T should be highlighted. Popular muscle cars of a compact class are Dodge Dart GT and Chevrolet Nova SS.
Among muscle cars of a classical type there following ones should be called: Dodge Challenger, Dodge Charger, Chevrolet Camaro, Chevrolet Monte Carlo, Dodge Dart GT, Ford Torino, Ford Fairlane, Mercury Cougar, Oldsmobile 442, Plymouth Barracuda, Plymouth Duster, Plymouth Road Runner, Plymouth Superbird, Pontiac GTO, Pontiac Firebird, Shelby Cobra.
Decline era

In the early 1970s, a fuel crisis broke out in the world, which stopped the wave of muscle cars development. Powerful, but very voracious cars had become useless to anyone. The last of the muscle cars in the best classical style was PontiacTransAm. Its production can be attributed to 1973-1974, after that no other manufacturer produced muscle cars in a classical sense. All companies either stopped production of their popular cars which were powerful in earlier times or significantly reduced engine power, "strangling" it for the sake of economy. All known models from this moment have turned into mediocre coupes, more affordable versions of luxury versions with mediocre dynamics and a loud name.
In addition, decline of the epoch of muscle cars was not only due to rise of a fuel price. The safety of cars with powerful engines, but with undercarriage and brakes from conventional road models was far from perfect. A huge number of fatal accidents caused the government to tighten security requirements. Muscle cars did not comply with these requirements, which predetermined their fate.
Currently, US companies have revived some models of muscle cars, of course, in modern interpretation. In the majority it is powerful cars, like: Dodge Charger, Chevrolet Camaro, Dodge Challenger, Ford Mustang.
To comment on the materials of the portal can only registered users. Log in.